Almost everyone, if not all, is shocked because of the new announcement regarding the content of a blog of which only AI-related topic will be accepted. After reading the update, I was thinking of the possible topics I can make and I know my fellow bitLanders family shares the same sentiment.
I admit that at first, it seems like the topic has been narrowed, literally yes it is, but, figuratively, it is not. Why? Well, AI is a diverse topic since it describes a set of different technologies. All we need to do is to understand precisely and completely what Artificial Intelligence is.
Before diving deeper, let's have an introduction first of what Artificial Intelligence is all about.

If you haven't read the announcement yet, kindly check Micky's recent blog post.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is defined as the science of training machines to perform human tasks. They are designed and programmed in such a way that the machines are capable to learn from experience, to think and act like a human and even adjust to new inputs.
Mentioned by the CEO of DataRobot, Jeremy Achin, in his keynote in Japan AI Experience 2017, "An AI is a computer system that is able to perform tasks that ordinarily require human intelligence. These artificial intelligence systems are powered by machine learning. Many of them are powered by machine learning, some of them are powered by specifically deep learning, some of them are powered by very boring things like just rules."
Image Credits: Hubspot via Youtube
History
With the increase of data volumes, advanced algorithms and improvements of power and storage capacity, AI has become more advanced and popular. But, the idea of artificial intelligence was born in the year 1955 by John McCarthy of MIT. Then, the field of AI research started in the year 1956 at a workshop at Dartmouth College. The founders and leaders were Allen Newell (CMU), Herbert Simon (CMU), John McCarthy (MIT), Marvin Minsky (MIT) and Arthur Samuel (IBM).
![]()
Image Credits: NVIDIA (but photo grabbed at futurism.com)
Early AI Research
1950s - explored topics like problem-solving and symbolic methods
1960s - the US Department of Defense took interest in this type of work and began training computers to mimic basic human reasoning
1970s - the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) completed street mapping projects
2003 - before Siri, there was Alexa or Cortana as an intelligent personal assistant
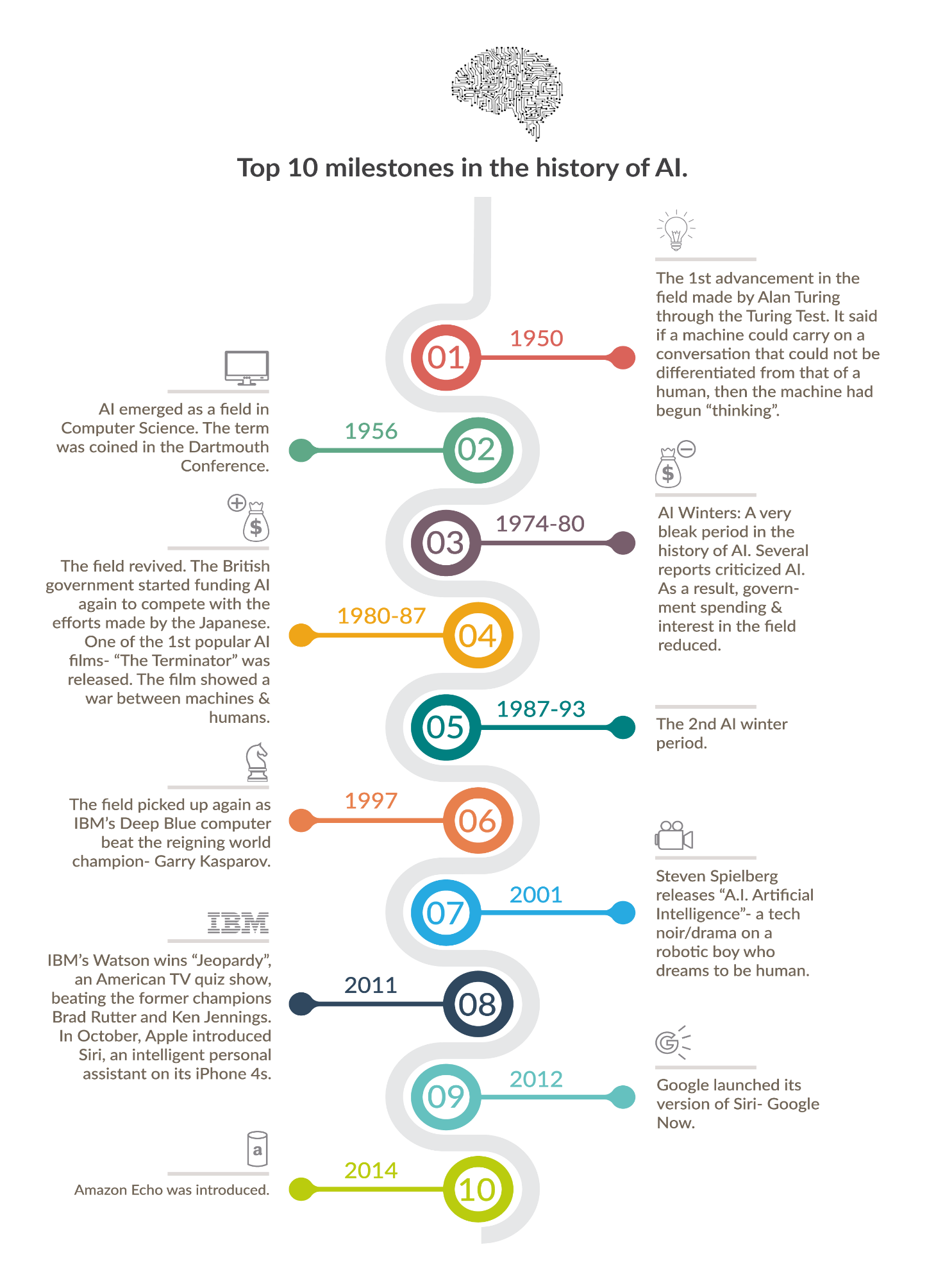
Image Credits: deckard.se
Types Of Artificial Intelligence
AI is categorized into two: Weak and Strong. Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is designed and trained for a particular task. An example is Siri from Apple. The other one is Strong AI, also known as artificial general intelligence. It is an AI system with generalized cognitive abilities hence, it is able to find a solution when presented with an unfamiliar task without human intervention.
On the other hand, an assistant professor from Michigan State University, Arend Hintze, categorized AI into four (4) types, from the existing AI systems up to the AI that does not exist yet.
Type 1: Reactive machine.
These AI has no memory and cannot use past experiences to inform future ones. An example is AlphaGO wherein it analyzes possible moves, both its own moves and its opponent, and then choose the most strategic move. We can say that Reactive Machine is a Weak AI.
Type 2: Limited Memory
These AI systems are capable of to learn and use past experiences for future decisions. An example is self-driving cars. Thus, this can be considered as Strong AI.
Type 3: Theory of Mind
This refers to the understanding that others have their own beliefs and intentions that impact the decisions this AI makes. This kind of AI does not yet exist.
Type 4: Self-awareness
From the word itself, the AI system has conscious knowledge of one's own character, feelings, motives, and desires. The machines will understand their current state and can use the information to infer what others are feeling. This type of AI does not yet exist.
Basic Components Of AI

Image Credits: innoplexus.com
When tackling Artificial Intelligence, it is inevitable that you will encounter different technical terms such as Machine Learning and Deep Learning. For that reason, understanding the AI jargon is the key to understand completely what AI is all about and how it works.
Now there are six (6) basic components of artificial intelligence:
1. Machine Learning: Learning from experience
2. Deep Learning: Self-educating machines
3. Neural Network: Making associations
4. Cognitive Computing: Making inferences from context
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding the language
6. Computer Vision: Understanding images
Machine Learning

Image Credits: vinodsblog.com
Machine Learning (ML) is a specific subset of AI that trains the machine the ability to learn from data, identify patterns and make decisions or predictions with minimal human intervention.
Example: Predicting or suggesting movies you might like in Netflix
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that trains a computer to perform human-like tasks such as voice and image recognition and then make predictions.
Example: Asking questions to Siri from Apple.

Image Credits: Amir Efrati
Neural Network
Neural Networks are computing systems with interconnected nodes, like neurons in the human brain. Neural networks enable deep learning using the algorithms that can recognize images and/or patterns and correlations in raw data. Over time, it continuously learns and improves.
Example: Inserting a set of 1000 dog images, the machine will process the inputs (images) and then it will produce a single output, answering the question, "Is the image a dog or not?"
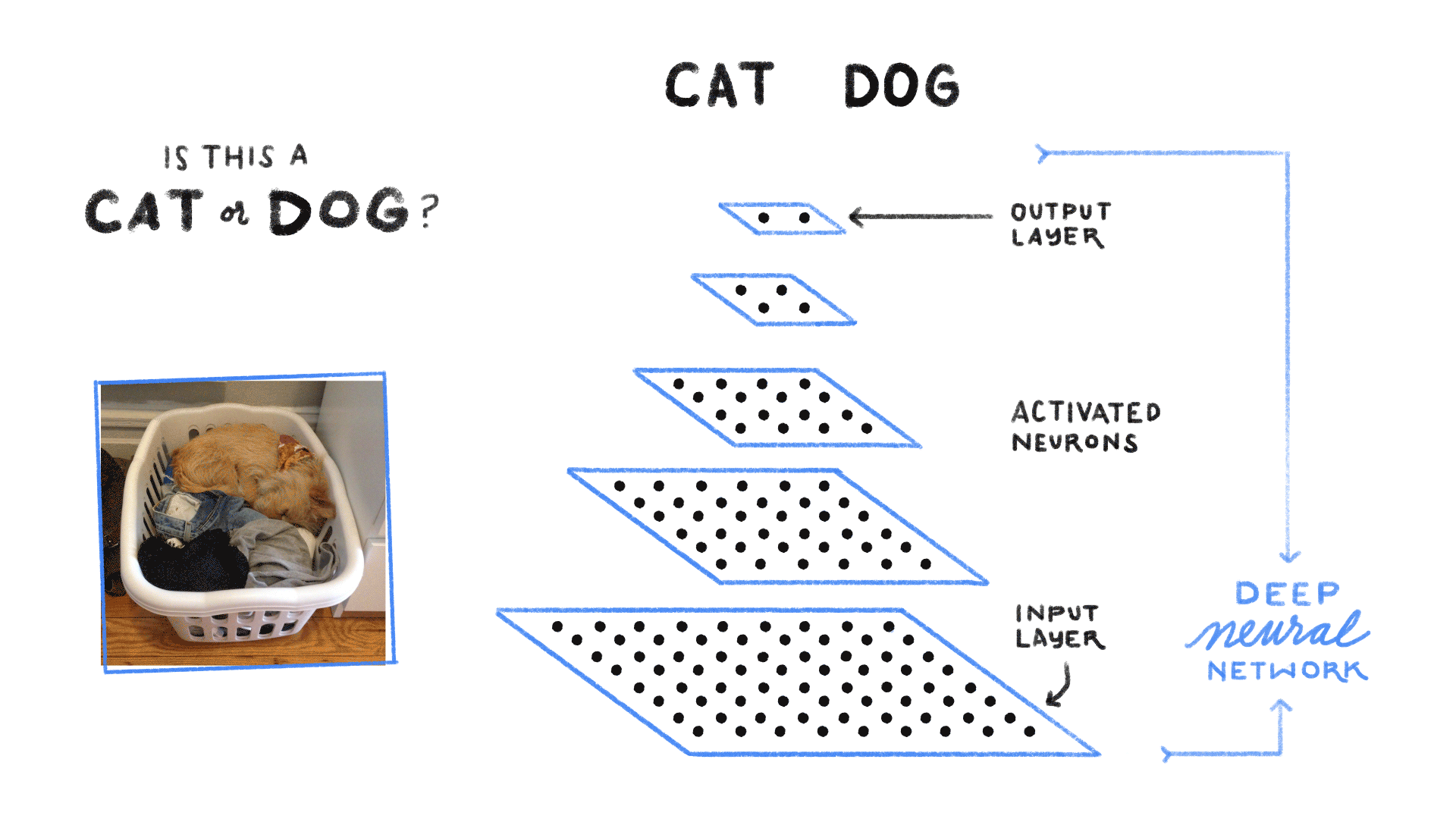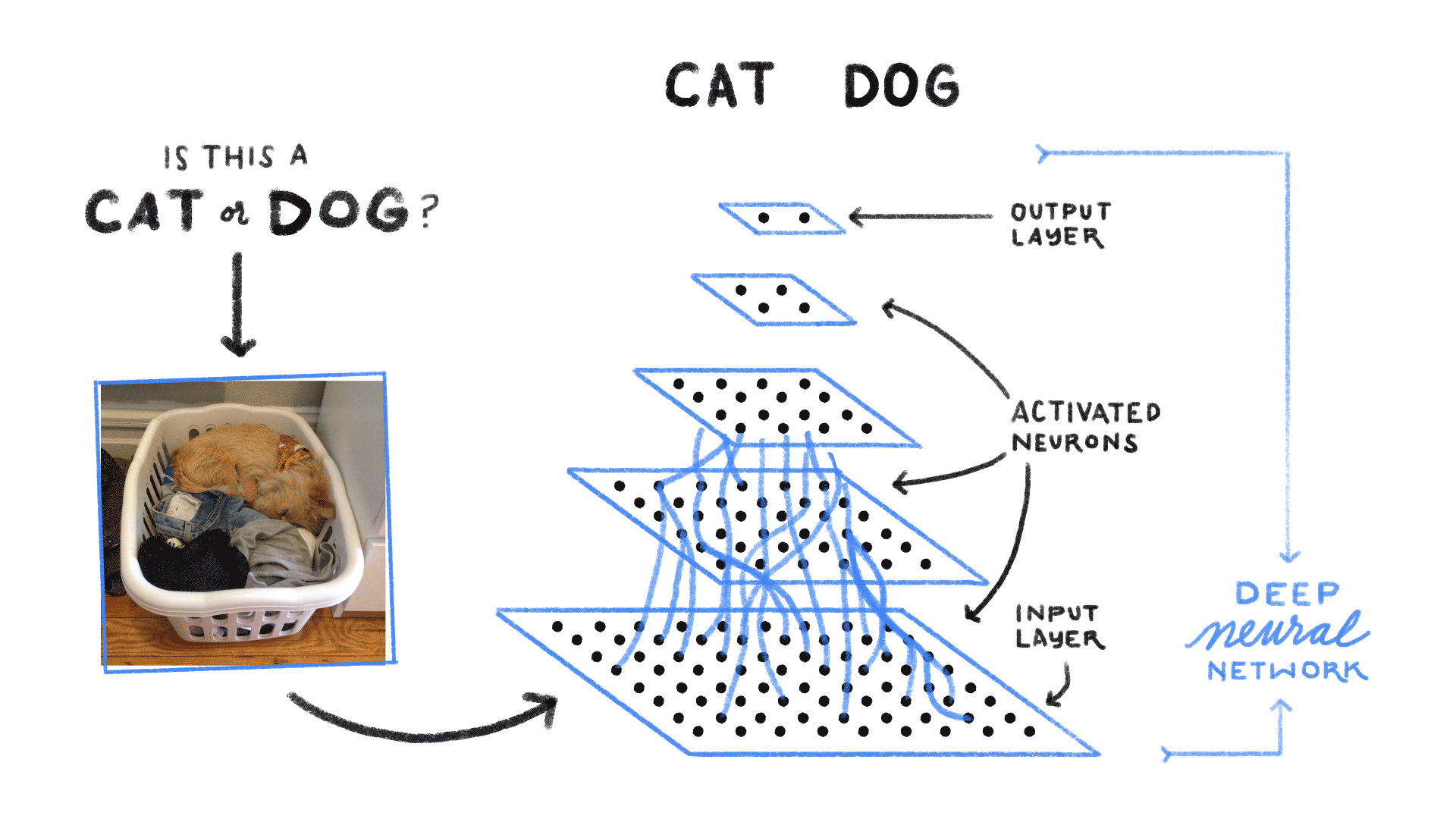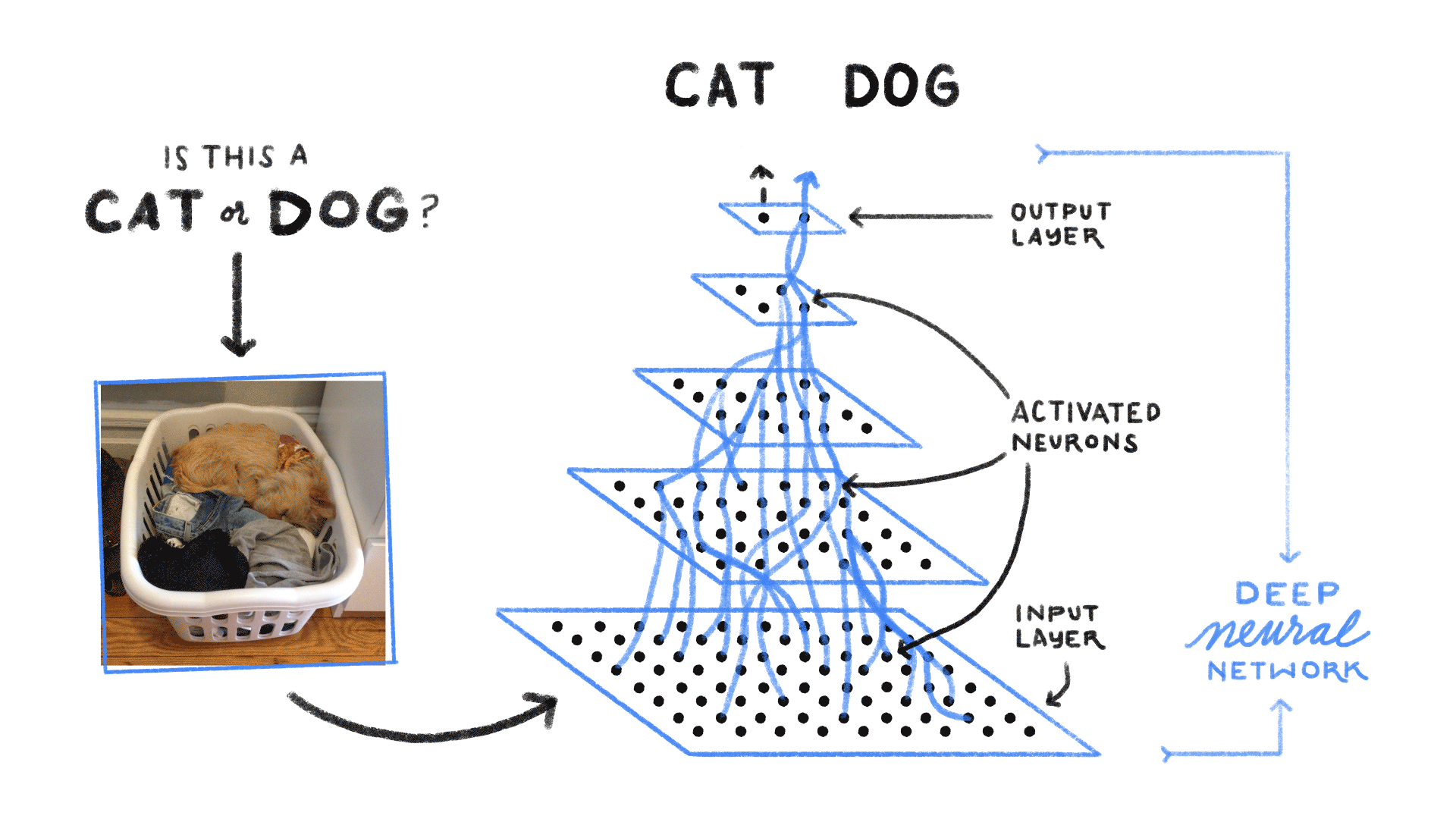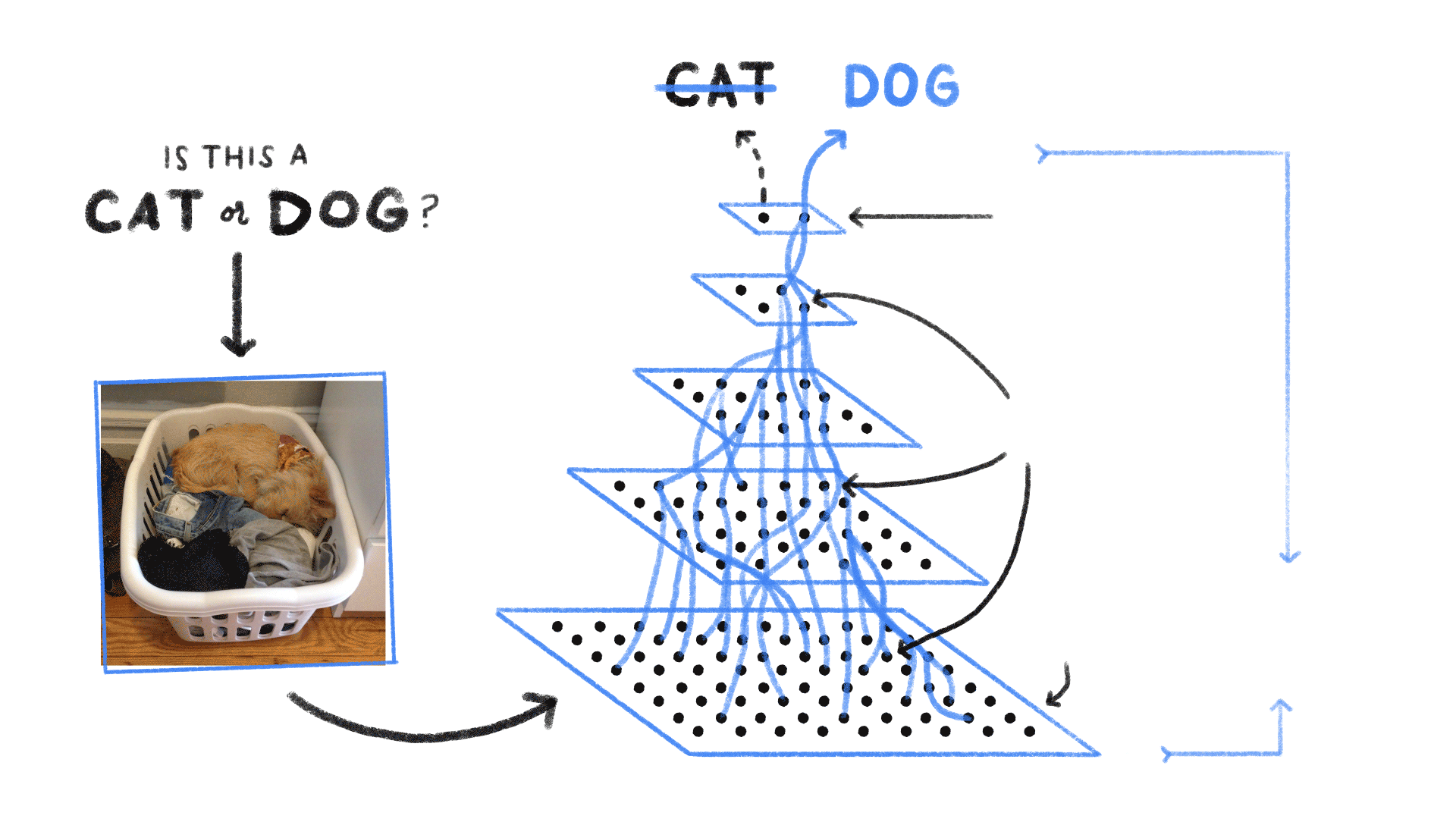
Image Credits: Medium
Cognitive Computing
Cognitive Computing imitates and improves machine and human interaction. It enables the machine to understand human language and the meaning of images. To mimic the way the human brain works, it uses self-learning technologies that utilize data mining, pattern recognition, and natural language processing (NLP).
Example: Medical equipment or diagnostic tools that assist doctors on how to treat their patient like the IBM Watson for Oncology, used at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, that provides oncologists with evidence-based treatment options for cancer patients.

Image Credits: smartsheet.com
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing is another subset of artificial intelligence that helps computers to analyze, understand and generate human language.
Example: Skype Translator that translates the speech of multiple languages in real time.

Image Credits: Microsoft
Computer Vision
Computer vision is the ability of machines to see, identify and process images. It relies on pattern recognition and deep learning to recognize the image in a picture or video.
Example: A car that can identify and distinguish obstacles or objects on and around the road such as traffic signs, traffic lights, and pedestrians and then act accordingly, like any driver on the road.
Summing Up
If we look around, we get to see a number of artificial intelligence applications such as surveillance cameras from stores and establishments, drones flying at the park or in an island owned by a travel vlogger and also, even just in our normal daily routine regardless the age, are already using artificial intelligence and one example is the smartphones.
Moreover, in this era of technological advancement, some of us are still unaware that the things we do involve artificial intelligence. It is a huge misconception that artificial intelligence applies to robots only because AI is continuously evolving exponentially for the benefit of mankind.
Image Credits: Raj Ramesh via Youtube
☀☀☀
THANKS FOR DROPPING BY!
☀☀☀
CARYL KEEN
☀☀☀
2019, All Rights Reserved.



