Erectile dysfunction—a persistent failure to achieve or sustain an erection—is a widespread problem; in the USA alone, estimates suggest there are around 18 million men who are afflicted. Achieving sexual arousal involves an intricate combination of brain, nerve endings, hormones, emotions, and blood vessels; it is not surprising that things can go wrong.
We are all probably familiar with some causes of erection failure: old age, smoking, alcohol misuse, and diabetes. But there are a number of other, more obscure factors that can contribute to the male member failing to rise to the occasion.
1.High Blood Pressure
To achieve an erection, the penis needs to be inflated with blood. We might reasonably expect that someone with high blood pressure would possess a more powerful pump to achieve this aim and therefore might be less likely than the average man to suffer erectile failure.
Research has shown, however, that around two-thirds of males with high blood pressure (a disorder known medically as “hypertension”) experience some degree of erectile dysfunction. Persistently high blood pressure is believed to damage the blood vessels that supply the penis, preventing their full expansion and consequently denying the penis a sufficient blood supply. In addition to impeding the ability to gain an erection, high blood pressure may also dampen sexual interest and prevent ejaculation.
2. Antidepressant Medication

We could be forgiven for assuming that pills that improve mood and counter misery would enhance a person’s sex life. But this is often not the case. Both the older type of antidepressant (the “tricyclics”) and the newer versions (the “SSRIs”) cause a range of sexual difficulties in both sexes, including erectile problems in males.
The reason for this unfortunate side effect is that antidepressants change the levels of our nervous system’s chemical messengers, such as serotonin and dopamine. This has the effect of dampening the sensitivity of the sexual organs and impairing both sexual interest and arousal. Serotonin may be particularly potent in this regard due to its inhibition of nitric oxide, a chemical that plays a central role in the relaxation of smooth muscle to allow blood flow to the penis.
3. Anabolic Steriods

Although steroids boost the level of testosterone and might therefore be expected to enhance sexual arousal, prolonged use interferes with the body’s natural production of the hormone. This has the effect of shrinking the testicles and increasing the risk of erectile failure. Awash with all this additional, artificially induced testosterone, natural producers of the male sex hormone become lazy. Therefore, when the person stops using anabolic steroids, the body is often rendered incapable of generating sufficient amounts of testosterone to achieve erections.
4. Peyronie’s Disease

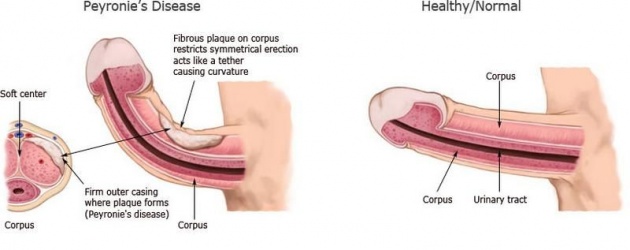
Peyronie’s disease is a disorder that afflicts around 1 percent of men. It involves the buildup of scar tissue along the penis, causing it to bend, painfully during the process of arousal, thereby softening the erection. The causes of the disorder are unknown, although experts believe it might be a combination of genetic inheritance and injury to the penis. The speed of onset of the disease varies considerably, ranging from very gradual to a rapid, overnight emergence.
In a non-aroused, flaccid state, the problem may not be apparent, but during erection pain is experienced and a bend in the penis becomes visible. In rare instances, the curvature can be severe. In up to 20 percent of the cases, the disorder will spontaneously rectify itself without treatment. The majority of sufferers, however, may require active intervention involving either medication or surgery.
-Taken from the original article by Gary L. Sidley-
-All credits to Gary L. Sidley and Listverse.com-



