At the beginning of the 20th century astronomers classified stars according to their pitch and spectrum, and found models that referred to the underlying physics.

The colors of the stars tell us about their temperature and chemistry, which is finally related to their mass.
If you look closely, you can see that the stars appear with many different colors, for example the sun is yellow, Betelgeuse is red, Arcturus is also yellow and Vega is white-blue.
But what do the colors tell us?
Temperature is the main cause of shades. The hottest stars have a blue appearance, and their surfaces can reach up to 40,000K is something like 39726. 85 C the coldest stars glow red and are only a few thousand degrees kelvin away. In the middle, when the atmospheres are progressively cooler, the colour of a star tends to white, yellow and orange.
Stellar Spectra
At the end of the 19th century, astronomers observed stellar light in greater detail, classifying it according to the constituents of their rainbows. The spectra of stars are scratched by dark lines where their light is absorbed by the chemical elements of the hot gases that envelop them. The cooler outer layers absorb the light produced by the warmer interior. Hydrogen is the most common element in stars, and therefore the signature of the lines of hydrogen absorption is more easily visible in the spectra.
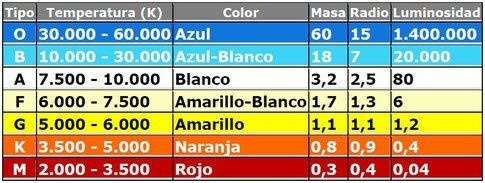
Classification
Astronomers have classified stars according to the characteristics of their light. Initially the stars were classified according to the intensity of several lines of absorption, but a more comprehensive approach was developed at the Hardvard observatory.
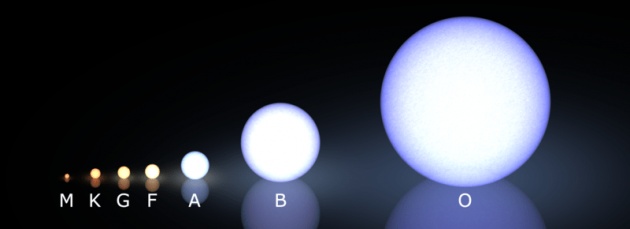
This classification is according to their temperatures, from the hottest with temperatures of up to 40,000 K to the coldest of about 2,000 K and are distributed in a sequence of types called with the letters O, B, A, F, G, K and M. So the O are the hottest and blueest and the M are the coldest and redest.

In astronomy the luminosity of stars is measured on a logarithmic scale because it covers a wide range. The brightest star Vega is estimated to have a magnitude of 0; the bright star Sirius has a magnitude of -1. 5; and other fainter stars have magnitudes of 1, 2 and so on..
Saluditos...



