
Photo Credit: Google
I would imagine our body as a complex group of factories working 24/7 to keep our body alive and working. Just as every factory makes use of different raw materials in order to produce all its signature products, our body also needs multiple raw materials to produce the substances needed to support our life.
In order for us to be able to live – to walk, talk, work, eat or do anything – every cell of our body must do their functions; like the intestines to digest the foods we ate, the blood to carry the nutrients to every cell and so on. All these functions are being done with the help of these so-called vitamins and minerals; which we must take in from outside sources, that is, from the foods we eat every day.
While most of us are very familiar with the various vitamins, like Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, and D, and E; we may not be familiar with another one named Vitamin K, which was only known not long ago.
I will try to discuss the importance of this little known vitamin for its important role in keeping our body healthy and strong.

Vitamin K, what is it?
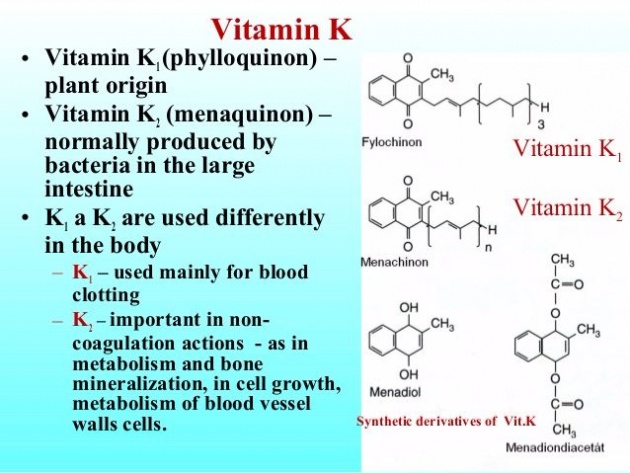
Vitamin K is a group of vitamins with similar structures.
Vitamin K derives its name from the word Koagulation , or coagulation which means to become thick or partly solid.
So as the name indicates, Vitamin K acts as an agent for the normal clotting of our blood. This means it helps the blood to clot to prevent excessive bleeding.
Vitamin K is a compound composed of K1 (phylloquinones), K2 (menaquinones), and K3 (menadiones).
The active blood-clotting agent, for long time, this is how Vitamin K is identified since it was discovered. But not so long ago, researchers have unveiled other important roles of Vitamin K in relations to bone building and cardiovascular health.
These issues I will discuss in part 2 of this article.

Photo Credit: www.pixabay.com
Why is clotting of blood important?
Whenever the skin is punctured, when it is cut or bruised, blood will flow continuously from the wound until the blood clots and the wound is sealed off; and then the bleeding stop. Otherwise, a person can bleed to death.
Vitamin K is needed for the blood to clot.
Deficiency in Vitamin K results in less ability of the blood to clot and this may cause excess bleeding from wounds and bleeding disorders, like blood in the urine and stools.
Where do we get Vitamin K?
Video Credit: www.youtube.com
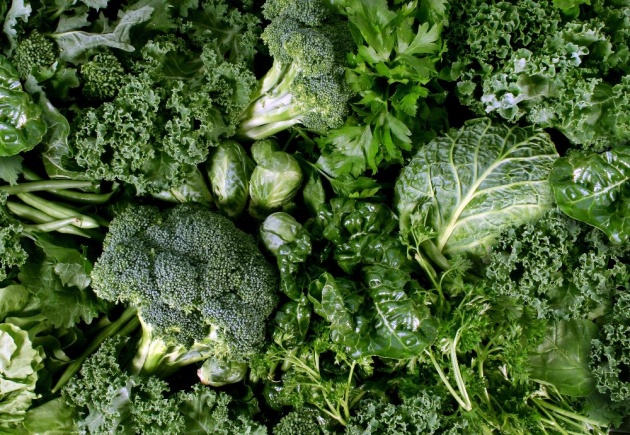
1. Vitamin K1 is found in Plant foods - where Vitamin K is needed for their photosynthesis.
It is found abundantly in dark green leafy vegetables, like Kale, cabbage, bok-choy, broccoli, spinach, mustard greens, turnips greens, Brussels sprouts, leafy lettuce, etc.
Other good sources are beans, soybeans, green peas, tomato, cucumber, cauliflower, asparagus, and leeks. K1 is also found in fruits like kiwi, avocado, strawberries, and grapes; and in black pepper, cilantro, basil, bell peppers, and sage, too.

Photo Credit: Google
Thus, Vitamin K1 may be considered as the “plant form” Vitamin K.
Increasing our intake of green leafy vegetables may result to increase of the level of Vitamin K in our body.
2. Vitamin K2 is readily found in foods produced or made from pastured and grass-fed animals, such as butter, eggs, chicken, beef, lamb, cheese, liver, and cow’s milk.
It is also available in fish, like tuna, salmon and sardines.
3. Vitamin K2 is found in our intestines, where they are made naturally by the friendly bacteria present in our guts by combining K1 and K3. This is our primary source.
Therefore, it is necessary that we maintain a substantial number of friendly bacteria in our guts, and regularly eat enough plant foods, especially the green leafy vegetables where K1 is abundant. Then we will have enough VitaminK2 and there will be no worry of deficiency in Vitamin K.
Friendly bacteria can be found in probiotic foods like yoghurt, or prebiotic supplement with digestive enzymes.
4. Vitamin K is also found in fermented foods. Fermented soy products, such as tempeh and miso, contain significant amount of Vitamin K2.
5. K3 are found in foods; but in very small amount only.
Causes of Vitamin K deficiency:

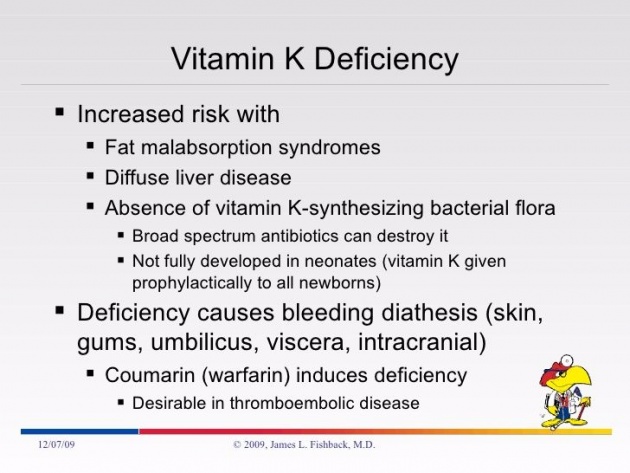
Photo Credit: Google
Although normally we may not worry about deficiency in Vitamin K, but there are instances when certain health issue may result in a deficiency and it may cause excessive and uncontrolled bleeding.
Some of the causes of deficiency in Vitamin K:
1. Persons who are on long-term antibiotics therapy may have deficiency in Vitamin K.
Antibiotics destroy the bacteria in our guts that produce Vitamin K, causing the deficiency. It is therefore advisable to take probiotic supplement to replace the friendly bacteria killed by the antibiotics.
2. Persons who are taking anti-coagulant or blood thinner drug may show deficiency of Vitamin K because these drugs deliberately block the ability of Vitamin K to make blood clotting proteins.
These blood thinner drugs are prescribed to people with higher risk of blood clotting; these are people who are at risk of heart attack, stroke, and deep vein thrombosis. These conditions are caused by blood clots that are formed in the veins these clots blocked the normal flow of blood in the body.
Taking anti-coagulant drugs in these cases needs careful monitoring because inhibiting too much may pose the risk for hemorrhagic stroke or bleeding somewhere else in the body.

Photo Credit: www.pixabay.com
These also includes persons who are taking medications that interfere with the effect of Vitamin K, such as antacids, aspirin, drugs for cancer, seizures, high cholesterol and other conditions.
It is advisable for these persons to follow doctor’s order regarding dietary intake of Vitamin K to avoid any serious complications.
However, Vitamin K is also used to counteract an overdose of blood thinner drugs. An overdose could trigger an excessive or uncontrolled bleeding.
3. Persons who have digestive diseases that affect absorption of Vitamin K in the digestive tracts, such as pancreatic dysfunction, Crohn’s disease and active Celiac disease may have deficiency in Vitamin K.
Vitamin K is a fat soluble Vitamin, any drug or disorder which interferes with absorption of fat will impair Vitamin K absorption, causing a deficiency.
4. Persons who have poor diet or who are severely malnourished may show deficiency of Vitamin K.
5. Persons who drink too much alcohol may also show signs of deficiency.
6. Newborn infants may suffer Vitamin K deficiency.
While deficiency of Vitamin K in adults is considered rare, it is common in newborn infants in the first few weeks of their life. It is because they still do not have the essential bacteria in their guts when they are born.
This deficiency may result in bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, like bloody stool or bloody vomiting.
However, a single injection of Vitamin K for newborn is given to correct this condition.

Photo Credit: Google
Do we need to take Vitamin K supplement?
Normally, it is not advisable to take Vitamin K supplement, unless prescribed by physician.
Since Vitamin K is easily acquired from natural foods, to maintain a normal level of Vitamin K, it is better to regularly take the following foods that are excellent and good sources of Vitamin K:
- Green leafy vegetables;
- Probiotic supplements for friendly bacteria;
- Fermented functional foods, such as yoghurt and fermented soy products
- Prebiotic supplements with digestive enzymes.
Although there is no reported toxicity for natural Vitamin K in adults, you should not use vitamin K supplements unless your health care provider tells you to.
The Vitamin is available in supplemental form, MK4 and MK7 MK4 has a short active time, while MK7 has a longer active time. This means you must take more of MK4 daily than MK7.

Photo Credit: www.pixabay.com
The other benefits of Vitamin K
There are a few important benefits from Vitamin K which I will discuss in part 2.
1. Some studies suggest that it helps maintain strong bones in the elderly.
Some have looked to vitamin K2 as possible treatment for osteoporosis and steroid-induced bone loss, and even cavities!
2. Some suggest use of vitamin K for treatment of cancer, symptoms of morning sickness, removal of spider veins, and other conditions.
Nature has provided us everything we need, among others the foods or substances that are required to sustain life and to keep our physical body in supreme condition. Therefore, in order to be healthy, one of the important things we must do is to know what is good for our body and to eat the right kinds of foods accordingly.
Video Credit: www.youtube.com
References used:
2. WebMD
4. Medline Plus



