Geological Investigation of the ground for Final Design:
- After having selected the site on the basis of preliminary Geological Investigation (i.e. carrying out reccy, geo-surveys, taking the ground-samples and testing the collected samples in the lab), detailed and final Geological Investigation is carried out
- For this purpose, additional and detailed boring and testing of the ground is carried out:
(i) In-Situ Soil Testing (is carried out in order to find out in-situ behavior and characteristics of the ground) – These tests will be studied in good detail in Soil Mechanics
(ii) Detailed boring of the sub-surface rock only – Rotary Drilling and Coring is carried out
- Depth of the ground-boring depends upon the type, size, life, purpose and area of the structure to be built
- In many situations and projects, the final and practical decisions
are made more on the basis of results of the field tests than results of the same ground-samples tested in the lab
Important Field Tests (Field Tests are also known as In-Situ Tests) Equipment of the first Four Tests is known as Penetrometer:
(i) Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
(ii) Static Cone Penetration Test (CPT)
(iii) Dynamic Cone Penetration Test (DCPT)
(iv) Cone Penetrometer using Physical Phenomena
(v) Vane Shear Test
(vi) Bearing Capacity Test
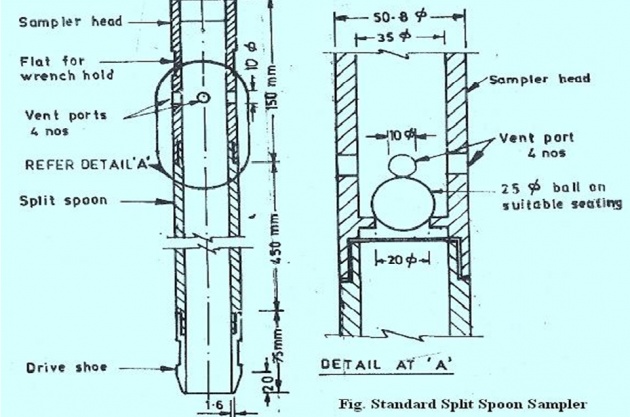
(i) Standard Penetration Test (SPT): Soil boring reports are not considered complete without the result of this test – a very important test
This test is carried out by driving a Standard Split Spoon Sampler (3 to 5 ft long, usually 3 ft long) inside an already made bore-hole, by usually a hydraulic hammer weighing 50 to 100 kg, usually 65 kg, dropping it through a height of half to one meter, usually ¾ of a meter i.e. 750 mm
The number of blows for every 75 mm penetration is counted until the sampler penetrates a depth of 450 mm. The result is divided into three sets of blows usually for every 150 mm penetration.
First set is neglected; second and third sets are reliable and taken into account. Number of blows for the last 300 mm are called N value for SPT. Chart showing N value for sand and soil:
N Value Consistency Unconfined Compressive Strength
0 – 4 Very loose sand Nil
10 – 30 Medium sand Nil
> 50 Very dense sand Nil
0 – 2 Very loose soil Nil
4 – 8 Medium soil 10 N (=10 kN/m2)
8 – 15 Stiff soil 13.5 N
> 30 Very hard soil > 20 N

(ii) Static Cone Penetration Test (CPT): Used for soft clays, silts and fine-sands only.In this test, pressure, denoted as Q(CPT) (usually expressed in kgf /cm2) required to push the cone of this equipment into the soil, is measured. This test is also known as Dutch Cone Penetration Test (but not called as DCPT which is Dynamic Cone Penetration Test) è Number of blows = NQ
- (iii) Dynamic Cone Penetration Test (DCPT):
- Equipment consists of penetrating cone with Apical Angle of 60O
- 50 mm cone dia test without circulating bentonite, for simple investigation
- 65 mm cone dia test with circulating bentonite, for detailed investigation
- 50 mm cone dia test same as Standard Split Spoon Test i.e. SPT
- 65 kg hammer drops through 750 mm height
- Number of blows for the cone to penetrate 300 mm is taken as Dynamic Cone Penetration Value: ND
- Blows count is taken for every 100 mm penetration of the cone