PROPAGATION MODELS:
when we talk about propagation model the first question raise in mind is what is propagation model..?
"propagation model are those models which are used to predict received signal strength at a given distance from transmitter as well as variability in received signal strength at close distance."
TYPES OF PROPAGATION MODEL:
1) large scale propagation model:
this model is used to estimate received signal strength for any arbitrary (T-R) separation and also used to estimate coverage area
2) small scale propagation model;
this model is used to predict the rapid fluctuation in received signal strength at short distance or shorter spin of time.
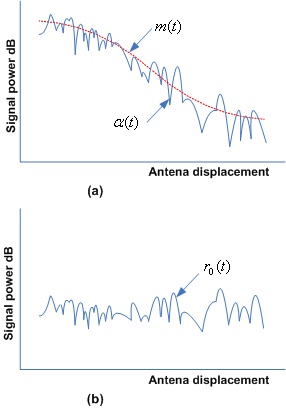
the above diagram shows received signal strength and rapid fluctuation in received signal..a(t) shows fluctuations which is predict by small scale propagation model while m(t) shows received signal strength which is predict by large scale propagation model.
3) free space propagation model:
this model is used to estimate received power at receiver.this model is used when signal travel in the free space between two BTS.
9818_fa_rszd.jpg)
power received can be find by following formula
Pr=Pt*Gt*Gr*(1/f)pw2/(4*pi*d)pw2*L
where
Pr= power received
Pt=power transmitted
Gt=gain of transmitter
Gr=gain of receiver
d= distance
1/f=wave length
in the above equation all are constant except 'd'.which means that power received depends on distance traveled by a signal.Pr is inversely proportional to the square of the distance..if distance increase power received will decrease.
path loss can be calculated by this formula
path loss =power transmitted-power received.
while in db form
path loss =10log Pt/Pr
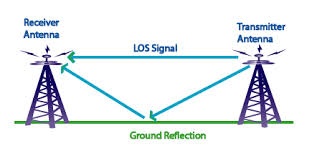
4)two way ground model:
this model is used to find received power of that signal which is reach at receiver not only directly from one BTS to another through air but also from ground which is reflected when strike to the ground.
for two ray ground model power received can be find by the formula
Pr = Pt*Gt*Gr*(ht)pw2*(hr)pw2/(d)pw4
where
pr = power received
pt=power transmitted
gt=gain of transmitter
gr=gain of receiver
hr=height of receiver
ht=height of transmitter
d=distance
in this formula Pr is inversely proportional to the double square of the distance.
now how a signal is propagate:.?
there are three basic propagation mechanism
1)reflection: reflection occur when wavelength of a signal is less then the dimension of striking object.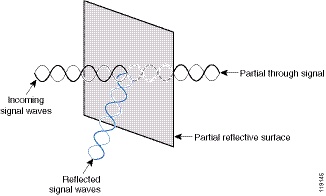
2)diffraction: this is occur when signal strike with sharp edge of an object.this sharp edge becomes source and signals are distributed from this source are of distributed signal have same wavelength.
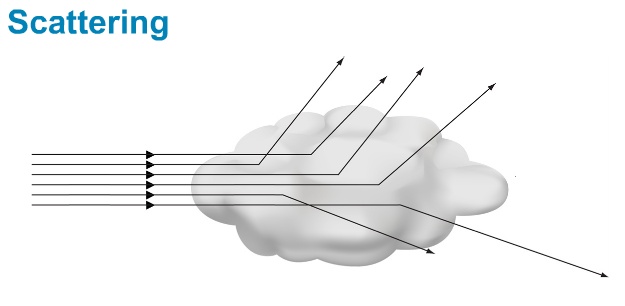
3)scattering: when wavelength of a signal is greater then dimension of single striking object but per unit volume of objects are greater then scattering occur. signal are scattered in to different direction but all does not have same wavelength like in diffraction.